Effect of Smoking on Oral Health
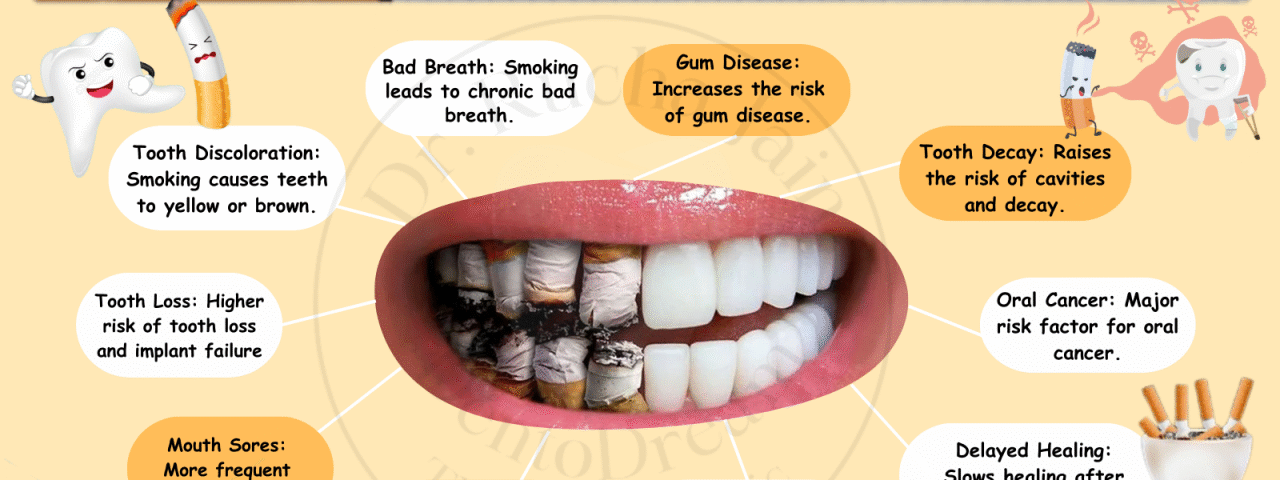
Smoking is one of the most harmful habits for the human body, and its damage starts directly from the mouth. The effect of smoking on oral health is serious and long-lasting, affecting teeth, gums, bones, and soft tissues. Many smokers ignore early signs because smoking hides symptoms, allowing oral diseases to worsen silently. Understanding how smoking harms oral health is essential for prevention and timely treatment.
Effects of smoking oral health
How Smoking Affects Oral Health?
The effect of smoking on oral health begins when toxic chemicals from tobacco enter the mouth. These chemicals reduce blood flow, lower oxygen levels, and weaken the immune response. As a result, the mouth becomes an ideal place for bacteria to grow.
Smoking affects oral health by:
-
Increasing plaque and tartar buildup
-
Reducing saliva production
-
Weakening gum tissues
-
Delaying healing
-
Increasing infection risk
Over time, these changes lead to severe dental and periodontal problems.
Smoking and Gum Problems
One of the earliest signs of the effect of smoking on oral health is gum damage. Smoking causes inflammation of the gums, but it also reduces bleeding, which hides the warning signs of gum disease.
Common gum problems caused by smoking include:
-
Gum redness and swelling
-
Gum recession
-
Deep periodontal pockets
-
Infection of gum tissues
For advanced gum and supporting tissue damage, read our detailed article on smoking and its effects on periodontium.
Effects of Smoking on Periodontium
Effect of Smoking on Teeth
Smoking has a direct negative effect on teeth appearance and strength. The effect of smoking on oral health includes visible and invisible tooth damage.
Tobacco-Stained Teeth
Nicotine and tar cause yellow or brown stains on teeth. These stains are difficult to remove with regular brushing.
Tooth Decay
Smoking increases harmful bacteria, leading to cavities and enamel damage.
Tooth Sensitivity
As gums recede, tooth roots become exposed, causing sensitivity and pain.
Smoking and Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Persistent bad breath is a common sign of the effect of smoking on oral health. Smoking dries the mouth and increases bacterial growth, which produces foul-smelling gases.
Causes of bad breath in smokers include:
-
Dry mouth
-
Gum disease
-
Tooth decay
-
Tongue coating
Effect of Smoking on Bone Supporting Teeth
Smoking weakens the jawbone that supports teeth. Reduced blood supply prevents bone regeneration, leading to bone loss. This is one of the most dangerous aspects of the effect of smoking on oral health.
Bone damage results in:
-
Loose teeth
-
Tooth mobility
-
Tooth loss
To understand bone damage in detail, read our complete guide on the effect of smoking on bone around teeth.
Effect of Smoking on Bone Around Teeth]
Delayed Healing After Dental Procedures
Another major effect of smoking on oral health is slow healing after dental treatments. Smokers often experience complications after:
-
Tooth extractions
-
Dental implants
-
Gum surgery
Smoking restricts blood flow, delays tissue repair, and increases infection risk.
Increased Risk of Oral Infections
Smoking weakens the body’s natural defense system. This makes smokers more vulnerable to:
-
Fungal infections (oral thrush)
-
Bacterial infections
-
Viral infections
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History
These infections can become severe if smoking continues.
Smoking and Oral Cancer Risk
The effect of smoking on oral health also includes a significantly increased risk of oral cancer. Tobacco damages DNA in mouth cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
Common areas affected by oral cancer:
-
Tongue
-
Lips
-
Gums
-
Cheeks
-
Throat
Early detection through regular dental visits is critical.
Common Oral Symptoms Smokers Should Watch For
Smokers are more likely to develop dental problems that show early warning signs. These symptoms should never be ignored:
-
Bleeding gums
-
Loose teeth
-
Persistent bad breath
-
Mouth sores
-
Gum recession
-
Jaw pain
These signs often indicate serious oral or periodontal disease.
Treatment Options for Smoking-Related Oral Problems
Treatment depends on the severity of damage caused by the effect of smoking on oral health.
Common treatments include:
-
Professional dental cleaning
-
Scaling and root planing
-
Medications for infection
-
Surgical periodontal treatment
-
Tooth replacement options
Stopping smoking improves treatment success.
Oral Hygiene Practices
-
Brush twice daily
-
Use fluoride toothpaste
-
Floss regularly
-
Clean the tongue
Diet and Hydration
-
Drink plenty of water
-
Eat calcium-rich foods
-
Avoid sugary snacks
Don’t Miss Dental Checkups
Regular dental visits help detect problems early and prevent severe damage.
Practical Tips to Quit Smoking
Quitting smoking is the best way to reverse the effect of smoking on oral health.
Helpful tips:
-
Set a quit date
-
Seek professional support
-
Use nicotine replacement therapy
-
Avoid triggers
-
Stay consistent
Why Regular Dental Visits Matter for Smokers?
Smokers should visit the dentist more frequently than non-smokers. Regular checkups help:
-
Detect gum disease early
-
Monitor bone loss
-
Screen for oral cancer
-
Improve long-term oral health
Conclusion
The effect of smoking on oral health is severe, progressive, and often irreversible if ignored. Smoking damages teeth, gums, bone, and soft tissues while increasing infection and cancer risk. Early awareness, proper oral care, regular dental visits, and quitting smoking are essential to protect oral and overall health.
For deeper insight into supporting structures of teeth, read our main article on effects of smoking on periodontium.
Effects of Smoking on Periodontium
2: Can smoking cause tooth loss?
Yes, smoking increases the risk of gum disease and bone loss, which are major causes of tooth loss.
Q3: Does smoking affect healing after dental procedures?
Yes, nicotine slows healing after extractions, implants, or gum surgery, increasing the risk of complications.
Q4: Can smoking cause bad breath or tooth staining?
Absolutely. Smoking leads to yellowing of teeth, buildup of plaque, and persistent bad breath.
Q5: Does smoking increase the risk of oral cancer?
Yes, long-term smoking is a major risk factor for oral cancers, including tongue, lips, and throat.
Q6: Can quitting smoking improve oral health?
Yes, quitting reduces the risk of gum disease, improves healing, and prevents further tooth and bone damage.
Q7: Are dental implants affected by smoking?
Yes, smokers have a higher risk of implant failure due to delayed healing and poor bone integration.