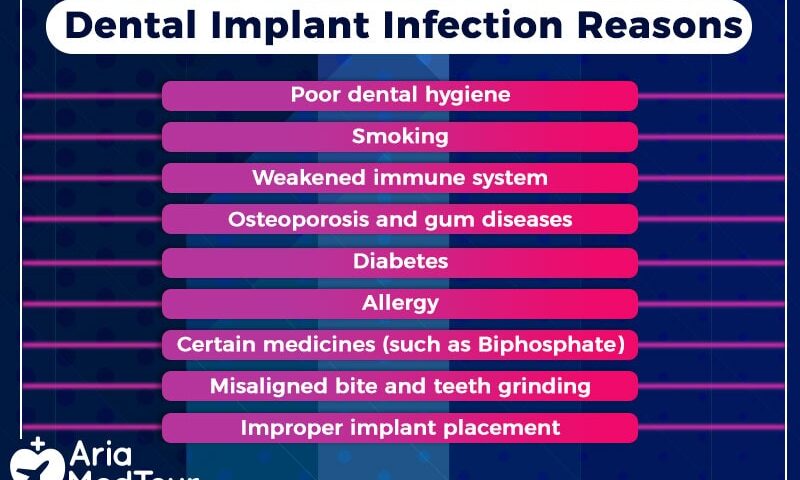
Dental Implant Failure Causes
Dental implants are a reliable solution for missing teeth, but their success depends on several oral and systemic factors. When these factors are ignored, dental implant failure may occur either early or years later.
Poor Osseointegration
Dental implant failure often occurs when proper osseointegration does not take place. Osseointegration is the process in which the implant fuses with the jawbone. If the bone quality is weak, bone volume is insufficient, or the implant moves during healing, the implant cannot become stable and may loosen or fail.
Infection (Peri-Implantitis)
Peri-implantitis is a serious infection that affects the gum and bone surrounding the implant. It is usually caused by poor oral hygiene, plaque buildup, or untreated gum disease. Over time, the infection leads to inflammation, bone loss, and eventual implant failure if not treated early.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking is a major risk factor for dental implant failure. Nicotine reduces blood supply to the gums, slows healing, and weakens the immune system. As a result, smokers experience delayed bone healing, higher infection rates, and increased bone loss around implants, leading to a higher failure rate.
Poor Bone Quality or Bone Loss
Healthy jawbone is essential for implant support. Bone loss may result from long-term tooth loss, osteoporosis, aging, or advanced gum disease. When bone density is low, the implant cannot achieve stability, and failure becomes more likely unless bone grafting is performed.
Improper Implant Placement
Incorrect placement of the implant can lead to uneven pressure during chewing. Poor surgical planning, wrong implant size, or incorrect angulation can damage surrounding structures and cause excessive stress on the implant, increasing the risk of failure.
Excessive Bite Force or Teeth Grinding
Teeth grinding or clenching places continuous pressure on dental implants. Unlike natural teeth, implants lack shock-absorbing ligaments, so excessive force can cause loosening, fracture of implant components, or bone loss over time.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting oral hygiene allows bacteria to accumulate around the implant. This leads to gum inflammation, infection, and bone loss. Without regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, even a well-placed implant can fail.
Medical Conditions and Systemic Diseases
Certain medical conditions interfere with healing and bone strength. Uncontrolled diabetes, autoimmune disorders, osteoporosis, and cancer treatments can reduce the body’s ability to support implants, increasing the risk of implant failure.
https://www.affordabledentures.com/blog/our-dental-expert-explains-dental-implant-failure
Poor Aftercare and Follow-Up
Failure to follow post-surgical instructions can delay healing and increase complications. Eating hard foods too early, missing follow-up visits, or not taking prescribed medications can negatively affect implant stability and long-term success.
Conclusion
Dental implant failure usually results from a combination of poor bone support, infection, lifestyle habits, and inadequate care. With proper planning, skilled placement, good oral hygiene, and regular follow-up, the risk of implant failure can be significantly reduced.
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene allows plaque and bacteria to collect around the implant. This leads to inflammation and infection of surrounding tissues, weakening implant support and causing failure over time.
2. Smoking Effects on Implant Health
Smoking restricts blood flow to the gums and delays healing. It increases infection risk and bone loss around implants, making smokers more likely to experience implant failure.
Smoking effects on gum diseases / Smoking effects on periodontium
3. Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
Untreated gum disease damages the gums and bone that support implants. A weak or infected periodontium cannot hold implants securely.
4. Insufficient Jaw Bone
Dental implants require adequate bone density. Bone loss caused by long-term tooth loss or periodontal disease can prevent proper implant fusion with the bone.
5. Poor Implant Placement
Incorrect positioning or angulation of implants causes uneven pressure during chewing. This stress damages surrounding bone and leads to implant loosening.
6. Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Excessive biting force or grinding puts pressure on implants. Since implants lack natural shock absorption, this force can cause implant failure.
Internal link idea: Teeth grinding and oral damage
7. Medical Conditions
Diseases like uncontrolled diabetes, osteoporosis, and immune disorders slow healing and increase infection risk, reducing implant success.
: Systemic diseases and dental health
8. Lack of Aftercare
Skipping follow-up visits allows small issues to worsen. Regular dental checkups help detect early signs of implant problems.
FAQs – Dental Implant Failure
1. What is the most common cause of dental implant failure?
Poor oral hygiene and gum infection are the leading causes.
2. Can smoking cause dental implant failure?
Yes, smoking increases infection risk and delays healing.
3. Can gum disease affect dental implants?
Yes, gum disease weakens implant support and leads to failure.
4. Can implants fail years later?
Yes, late implant failure can occur due to poor care or bone loss.
5. How can implant failure be prevented?
Good oral hygiene, quitting smoking, and regular dental visits help prevent failure.