Smoking and Its Effect on periodontium
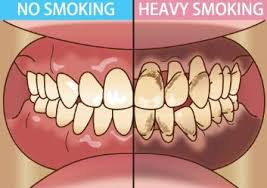
Smoking and its effect on periodontium is a serious oral health concern that many people ignore. The periodontium includes the gums, periodontal ligament, cementum, and bone around the teeth. These tissues play a vital role in keeping teeth strong and stable. When a person smokes, harmful chemicals directly damage these supporting structures.
Smoking not only stains teeth or causes bad breath but also silently destroys gum tissue and bone. The effect of smoking on oral health often progresses slowly, which is why many smokers do not notice the damage until it becomes severe.
effect of smoking on oral health)
What Is Periodontium?
The periodontium is the group of tissues that surround and support the teeth. It includes:
- Gingiva (Gums) – protect teeth from bacteria
- Periodontal Ligament – connects teeth to bone
- Cementum – covers the tooth root
- Alveolar Bone – holds teeth firmly in place
Healthy periodontium is essential for chewing, speaking, and overall oral health.
How Smoking Affects Gum Health
Smoking is one of the leading causes of gum disease. Chemicals in cigarette smoke reduce blood flow to the gums. When gums do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, they become weak and infected easily.
This strong relationship between smoking and gum disease explains why smokers experience more severe periodontal problems than non-smokers.
🔗 (Internal link here: smoking and gum disease)
Reduced Blood Flow to Gums
Smoking narrows blood vessels, which limits healing and hides early warning signs like bleeding.
Suppressed Immune Response
Smoking weakens the immune system, allowing bacteria to grow rapidly around the gums.
Effect of Smoking on Bone Around Teeth
The effect of smoking on bone around teeth is one of the most dangerous outcomes of smoking. The alveolar bone supports the teeth, but smoking reduces oxygen supply and damages bone-forming cells.
As a result:
- Bone breaks down faster
- New bone formation slows
- Teeth lose stability
🔗 (Internal link here: effect of smoking on bone around teeth)
Over time, bone loss leads to loose teeth and eventual tooth loss.
Smoking and Periodontal Pocket Formation
When gums pull away from teeth, deep pockets form between the gums and teeth. These pockets trap bacteria and plaque. Smoking increases pocket depth and infection severity.
Because smoking reduces pain and bleeding, these pockets often go unnoticed until serious damage occurs.

Passive Smoking and Periodontal Health
Passive smoking also harms oral tissues. People exposed to cigarette smoke inhale toxic chemicals that irritate gums and increase bacterial growth.
Children and non-smokers exposed to smoke face higher risks of gum inflammation and periodontal disease. The passive smoking effects on oral health are often underestimated.
🔗 (Internal link here: passive smoking effects on oral health)
Long-Term Effects of Smoking on Periodontium
The long-term effects of smoking on periodontal health include:
- Chronic periodontitis
- Severe bone loss
- Delayed healing
- Repeated gum infections
🔗 (Internal link here: long-term effects of smoking)
Long-term smokers often require complex and costly dental treatments.
Smoking and Tooth Loss
Smoking and tooth loss are closely connected. When gums and bone weaken, teeth lose support and become loose. Many smokers lose teeth earlier in life compared to non-smokers.
🔗 (Internal link here: smoking and tooth loss)
Tooth loss affects chewing, speech, appearance, and self-confidence.
Smoking and Dental Implant Failure
Dental implants need strong bone and healthy gums. Smoking increases the risk of implant failure by reducing blood flow and delaying healing.
Smoking is a major contributor to dental implant failure causes, especially due to bone loss and infection.
🔗 (Internal link here: dental implant failure causes)
Can Periodontal Damage Be Reversed?
Early gum disease can be controlled with treatment and by quitting smoking. However, advanced bone loss is often permanent. This makes prevention and early diagnosis extremely important.
Benefits of Quitting Smoking for Periodontal Health
Quitting smoking leads to:
- Improved blood flow to gums
- Faster healing after treatment
- Reduced infection risk
- Slower bone loss
Learning how to quit smoking naturally is one of the best ways to protect periodontal health.
🔗 (Internal link here: how to quit smoking naturally)
Prevention Tips
- Stop smoking
- Brush and floss daily
- Visit the dentist regularly
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Manage stress effectively
Conclusion
Smoking and its effect on periodontium is a major cause of gum disease, bone loss, and tooth loss. Smoking weakens gums, damages bone, reduces healing ability, and increases infection risk. Both active and passive smoking negatively affect periodontal health.
Quitting smoking and maintaining good oral hygiene are the most effective ways to protect the periodontium and preserve natural teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does smoking cause periodontal disease?
Yes, smoking is one of the biggest risk factors for periodontal disease due to reduced blood flow and weak immune response.
Can gums heal after quitting smoking?
Yes, gum health improves after quitting, but severe bone loss may not fully recover.
Why do smokers not notice gum bleeding?
Smoking reduces blood supply, hiding early signs like bleeding and swelling.
Is passive smoking harmful to gums?
Yes, passive smoking increases gum inflammation and periodontal disease risk.
FAQ – Periodontium
1. What is periodontium?
Periodontium is the supporting structure of the teeth. It helps hold teeth firmly in the jaw and keeps them healthy.
2. What are the main parts of the periodontium?
The periodontium includes gums (gingiva), periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone.
3. Why is the periodontium important?
It supports teeth, absorbs chewing pressure, and protects teeth from loosening or falling out.
4. What happens when the periodontium becomes unhealthy?
Unhealthy periodontium can cause gum disease, bleeding gums, bone loss, and tooth loss.
5. What causes damage to the periodontium?
Poor oral hygiene, plaque buildup, smoking, diabetes, and lack of dental care can damage the periodontium.
6. How does smoking affect the periodontium?
Smoking reduces blood flow to gums, weakens immunity, and increases the risk of periodontal disease.
7. What are signs of periodontium problems?
Bleeding gums, bad breath, gum swelling, loose teeth, and receding gums are common signs.
8. Can periodontium disease be treated?
Yes, with proper oral hygiene, professional dental cleaning, and early treatment, periodontium disease can be controlled.
9. How can we keep the periodontium healthy?
Brushing twice daily, flossing, quitting smoking, and regular dental checkups help maintain a healthy periodontium.
