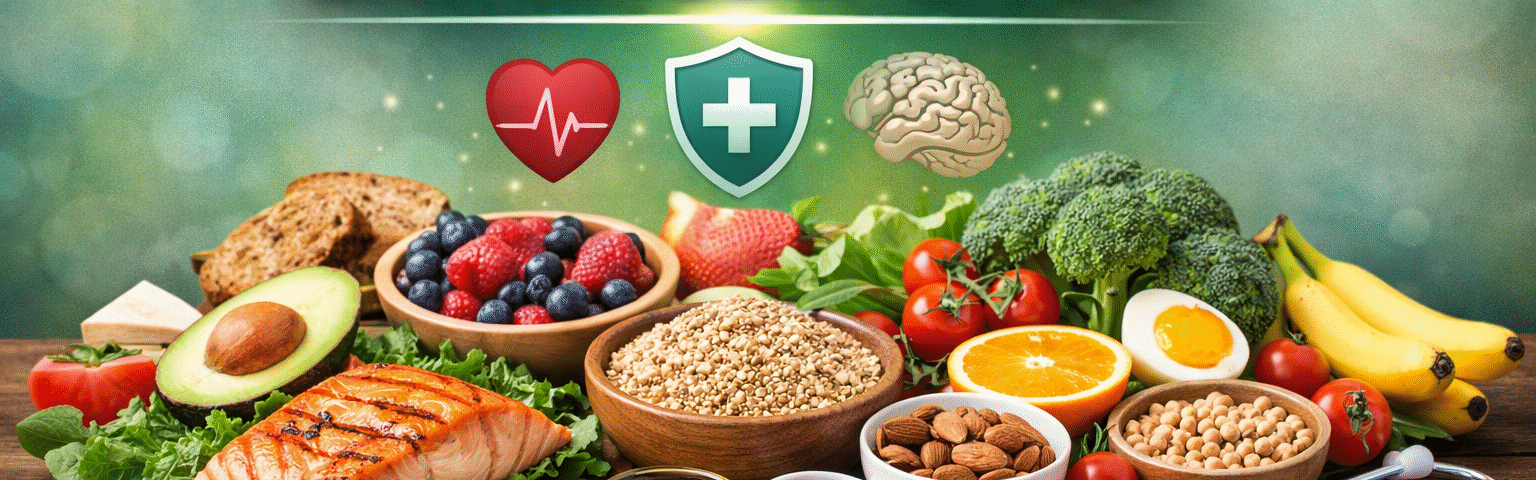
The importance of a balanced diet is essential for maintaining good health and daily energy. From long experience in health writing, it is clear that people who eat balanced meals feel more active, focused, and protected from illness. A balanced diet provides the body with the right nutrients in the right amounts.
A balanced diet is very important for maintaining good health and overall wellbeing. It provides essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that the body needs to function properly. Eating a variety of foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats not only strengthens the immune system but also supports growth and keeps the body active. A proper diet improves digestion, mental focus, and energy levels, helping us lead a healthy and productive life.
healthy digestion tips
Provides Essential Nutrients
One major reason of esential is that it supplies all essential nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Each nutrient has a specific role in keeping the body healthy. When these nutrients work together, the body performs its functions smoothly.easly to understand this read this article
Nutrient-Rich Foods for Daily Health
Supports Steady Energy Levels
A balanced diet helps maintain steady energy throughout the day. Carbohydrates provide quick energy, while healthy fats offer long-lasting fuel. Proteins support muscle strength and recovery. This balance prevents sudden tiredness and weakness.

Healthy Breakfast Ideas For Students And Children To Stay Active And Smart:
Improves Digestion and Metabolism
Another key is improved digestion. Fiber-rich foods support gut health and prevent digestive issues. A well-balanced diet also keeps metabolism active, helping the body use energy efficiently.
A balanced diet supports a healthy digestive system and improves metabolism. Fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains help the stomach function smoothly. Proper nutrients enable the body to convert food into energy more efficiently. As a result, problems like gas, constipation, and slow metabolism can be reduced.
weightl lose with banana
Strengthens the Immune System
A balanced diet strengthens the immune system by supplying vitamins and minerals that protect against infections. Regular intake of nutritious foods helps the body recover faster from illness and reduces the risk of frequent sickness.
Helps Maintain Healthy Weight
The importance of a balanced diet is also seen in weight management. Eating balanced meals reduces overeating and controls unhealthy cravings. This lowers the risk of obesity and related health problems.
Why Consuming Healthy Fats Supports Weight Control:
Supports Mental and Emotional Health
Balanced nutrition supports brain function and emotional stability. Proper nutrients improve concentration, reduce stress, and support better mood. People who eat well often feel more mentally active and positive.
Reduces Risk of chronic diseases
One long-term importance of a balanced diet is disease prevention. Healthy eating habits reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Balanced nutrition protects overall health over time.
 in conclusion, the importance of a balanced diet lies in its ability to support energy, immunity, digestion, mental health, and disease prevention. A balanced diet helps the body function efficiently and leads to a healthier and more active life.
in conclusion, the importance of a balanced diet lies in its ability to support energy, immunity, digestion, mental health, and disease prevention. A balanced diet helps the body function efficiently and leads to a healthier and more active life.
portance of a balanced diet is essential for maintaining good health and daily energy. From long experience in health writing, it is clear that people who eat balanced meals feel more active, focused, and protected from illness. A balanced diet provides the body with the right nutrients in the right amounts.
https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/how-to-eat-a-balanced-diet/eating-a-balanced-diet/
Provides Essential Nutrients
One major importance of a balanced diet is that it supplies all essential nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Each nutrient has a specific role in keeping the body healthy. When these nutrients work together, the body performs its functions smoothly.
Supports Steady Energy Levels
A balanced diet helps maintain steady energy throughout the day. Carbohydrates provide quick energy, while healthy fats offer long-lasting fuel. Proteins support muscle strength and recovery. This balance prevents sudden tiredness and weakness.
How Mint Helps Reduce Belly Fat and Boost Metabolism
Improves Digestion and Metabolism
Another key importance of a balanced diet is improved digestion. Fiber-rich foods support gut health and prevent digestive issues. A well-balanced diet also keeps metabolism active, helping the body use energy efficiently.
Strengthens the Immune System
A balanced diet strengthens the immune system by supplying vitamins and minerals that protect against infections. Regular intake of nutritious foods helps the body recover faster from illness and reduces the risk of frequent sickness.
A balanced diet plays a key role in strengthening the immune system. Foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, help the body fight infections and stay healthy.
The Importance of balance diet
Helps Maintain Healthy Weight
The importance of a balanced diet is also seen in weight management. Eating balanced meals reduces overeating and controls unhealthy cravings. This lowers the risk of obesity and related health problems.
Supports Mental and Emotional Health
Balanced nutrition supports brain function and emotional stability. Proper nutrients improve concentration, reduce stress, and support better mood. People who eat well often feel more mentally active and positive.
Reduces Risk of Chronic Diseases
One long-term importance of a balanced diet is disease prevention. Healthy eating habits reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Balanced nutrition protects overall health over time.
Daily Habits For A Healthy Heart And Balanced Blood Pressure:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the importance of a balanced diet lies in its ability to support energy, immunity, digestion, mental health, and disease prevention. A balanced diet helps the body function efficiently and leads to a healthier and more active life.
F A Q about the Importance of a Balanced Diet
1. What is meant by a balanced diet?
A balanced diet means eating different types of foods in the right amounts to provide all essential nutrients for the body.
2. Why is the importance of a balanced diet necessary for daily life?
The importance of a balanced diet is necessary because it supports energy, strength, immunity, and proper body function.
3. How does a balanced diet affect energy levels?
A balanced diet provides steady energy by combining carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats, preventing tiredness.
4. Can a balanced diet improve digestion?
Yes, fiber-rich foods in a balanced diet improve digestion and help the body absorb nutrients better.
5. Why is a balanced diet important for mental health?
Balanced nutrition supports brain function, improves focus, and helps manage stress and mood.
6. Is the importance of a balanced diet higher for children and students?
Yes, the importance of a balanced diet is higher for children and students because it supports growth, learning, and immunity.
7. Can a balanced diet help prevent diseases?
Yes, a balanced diet lowers the risk of heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and other chronic illnesses.
8. How does a balanced diet help in weight management?
A balanced diet controls hunger, reduces unhealthy cravings, and helps maintain a healthy weight.

